PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF PREGNANCY
Presumptive signs and symptoms of pregnancy are those signs and symptoms that are usually noted by the patient, which impel her to make an appointment with a physician. These signs and symptoms are not proof of pregnancy but they will make the physician and woman suspicious of pregnancy.
Amenorrhea
(Cessation of Menstruation). Amenorrhea is one of the earliest clues of pregnancy. The majority of patients have no periodic bleeding after the onset of pregnancy. However, at least 20 percent of women have some slight, painless spotting during early gestation for no apparent reason and a large majority of these continue to term and have normal infants.
Other causes for amenorrhea must be ruled out, such as:
- Menopause.
- Stress (severe emotional shock, tension, fear, or a strong desire for a pregnancy).
- Chronic illness (tuberculosis, endocrine disorders, or central nervous system abnormality).
- Anemia.
- Excessive exercise.
Nausea and Vomiting
Also called morning sickness.
- Usually occurs in early morning during the first weeks of pregnancy.
- Usually spontaneous and subsides in 6 to 8 weeks or by the twelfth to sixteenth week of pregnancy.
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum. This is referred to as nausea and vomiting that is severe and lasts beyond the fourth month of pregnancy. It causes weight loss and upsets fluid and electrolyte balance of the patient.
- Nausea and vomiting are unreliable signs of pregnancy since they may result from other conditions such as:
- Gastrointestinal disorders (hiatal hernias, ulcers, and appendicitis).
- Infection (influenza and encephalitis).
- Emotional stress, upset (anxiety and anorexia nervosa).
- Indigestion.
Frequent Urination.
- Frequent urination is caused by pressure of the expanding uterus on the bladder.
- It subsides as pregnancy progresses and the uterus rises out of the pelvic cavity.
- The uterus returns during the last weeks of pregnancy as the head of the fetus presses against the bladder.
- Frequent urination is not a definite sign since other factors can be apparent (such as tension, diabetes, urinary tract infection, or tumors)
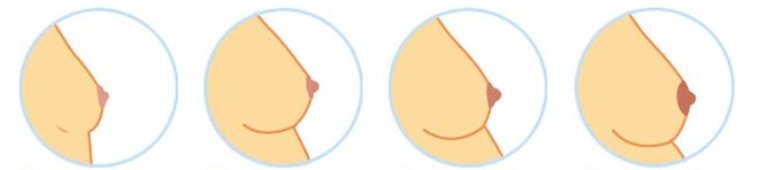 |
| Changes of the Breast during pregnancy - photo by The Alpha Parent |
Breast Changes
- In early pregnancy, changes start with as light, temporary enlargement of the breasts, causing a sensation of weight, fullness, and mild tingling.
- As pregnancy continues the patient may notice:
- Darkening of the areola - the brown part around the nipple.
- Enlargement of Montgomery glands – the tiny nodules or sebaceous glands within the areola.
- Increased firmness or tenderness of the breasts.
- More prominent and visible veins due to the increased blood supply.
- Presence of colostrum (thin yellowish fluid that is the precursor of breast milk). This can be expressed during the second trimester and may even leak out in the latter part of the pregnancy.
Vaginal Changes
- Chadwick's sign: This is where the vaginal walls take on a deeper color caused by the increased vascularity because of increased hormones. It is noted at the sixth week when associated with pregnancy. It may also be noted with a rapidly growing uterine tumor or any cause of pelvic congestion.
- Leukorrhea. This is an increase in the white or slightly gray mucoid discharge that has a faint musty odor. It is due to hyperplasia of vaginal epithelial cells of the cervix because of increased hormone level from the pregnancy. Leukorrhea is also present in vaginal infections.
Quickening (Feeling of Life).
- This is the first perception of
fetal movement within the uterus. It usually occurs toward the end of the fifth
month because of spasmodic flutter.
(a)A multigravida (someone who has had more than 1 pregnancies) can feel quickening as early as 16 weeks.(b) A primigravida usually cannot feel quickening until after 18 weeks.
- Once quickening has been established, the patient should be instructed to report any instance in which fetal movement is absent for a 24-hour period.
- Fetal movement early in pregnancy is frequently thought to be gas.
Skin Changes.
- Striae Gravidarum (stretch marks): These
are marks noted on the abdomen and/or buttocks.
(a) These marks are caused by increased production or sensitivity to adrenocortical hormones during pregnancy, not just weight gain.
(b) These marks may be seen on a patient with Cushing's disease or a patient with sudden weight gain.
- Linea Nigra.
(a) This is a black line in the midline of the abdomen that may run from the sternum orumbilicus to the symphysis pubis.
(b) This appears on the primigravida by the third month and keeps pace with the rising height of the fundus.
(c) The entire line may appear on the multigravida before the third month.
(d) This may be a probable sign if the patient has never been pregnant.
- Chloasma: This is called the "Mask of Pregnancy." It is a bronze type of facial coloration seen more on dark-haired women. It is seen after the sixteenth week of pregnancy.
- Fingernails: Some patients note marked thinning and softening by the sixth week.
- Fatigue. This is a common complaint by most patients during the first trimester. Fatigue may also be a result of anemia, infection, emotional stress, or malignant disease.
- Positive Home Test. These tests may not always be accurate, however, they are very effective today if they are performed properly.
PROBABLE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY
Probable signs of pregnancy are those signs commonly noted by the physician upon examination of the patient. These signs include uterine changes, abdominal changes, cervical changes, basal body temperature, positive pregnancy test by physician, and fetal palpation.
Uterine Changes.
- Position: By the twelfth week, the uterus rises above the symphysis pubis and it should reach the xiphoid process by the 36th week of pregnancy. These guidelines are fairly accurate only as long as pregnancy is normal and there are no twins, tumors, or excessive amniotic fluid.
- Size: The uterine increases in
width and length approximately five times its normal size. Its weight increases
from 50grams to 1,000 grams.

Hegar's Sign - Photo by Cure Cancer - Hegar's sign: This is softening of
the lower uterine segment just above the cervix. When the uterine is compressed
between examining fingers, the wall feels tissue paper thin. The physician will
use bimanual maneuver simultaneously (abdominal and vaginal) and will cause the
uterus to tilt forward. The Hegar's sign is noted by the
sixth to eighth week of pregnancy.

Ballottement - Ballottement: This is demonstrated during the bimanual exam at the 16th to 20th week. Ballottement is when the lower uterine segment or the cervix is tapped by the examiner's finger and left there, the fetus floats upward, then sinks back and a gentle tap is felt on the finger. This is not considered diagnostic because it can be elicited in the presence of ascites or ovarian cysts.
- Abdominal Changes. This corresponds to changes that occur in the uterus, as the uterus grows the abdomen gets larger. Abdominal enlargement alone is not a sign of pregnancy. Enlargement may be due to uterine or ovarian tumors, or edema.
Striae gravidarum may also be classifiedas a probable sign of pregnancy by the physician.
Cervical Changes
- Goodell's sign. The cervix is normally firm like the cartilage at the end of the nose. The Goodell's sign is when there is marked softening of the cervix. This is present at 6 weeks of pregnancy.
- Formation of a mucous plug. This is due to hyperplasia of the cervical glands as a result of increased hormones. It serves to seal the cervix of the pregnant uterus and to protect it from contamination by bacteria in the vagina. The mucous is expelled at the end of pregnancy near or at the onset of labor.
- Braxton-Hick's contractions. This involves painless uterine contractions occurring throughout pregnancy. It usually begins about the 12th week of pregnancy and becomes progressively stronger. These contractions will, generally, cease with walking or other forms of exercise. The Braxton-Hick's contractions are distinct from contractions of true labor by the fact that they do not cause the cervix to dilate and can usually be stopped by walking.
Basal Body Temperature
Positive Pregnancy Test by the Physician
Fetal Palpation
POSITIVE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY
Positive signs of pregnancy are those signs that are definitely confirmed as a pregnancy. They include fetal heart sounds, ultrasound scanning of the fetus, palpation of the entire fetus, palpation of fetal movements, x-ray, and actual delivery of an infant.
- Fetal Heart Sounds: The fetal heart begins beating by the 24th day following conception. It is audible with a Doppler by 10 weeks of pregnancy and with a fetoscope after the 16th week. It is not to be confused with uterine souffle or swishlike tone from pulsating uterine arteries. The normal fetal heart rate is 120 to 160 beats per minute.
- Ultrasound Scanning of the Fetus: The gestation sac can be seen and photographed. An embryo as early as the 4th week after conception can be identified. The fetal parts begin to appear by the 10th week of gestation.
- Palpation of the Entire Fetus: Palpation must include the fetus head, back, and upper and lower body parts. This is a positive sign after the 24th week of pregnancy if the woman is not obese.
- Palpation of Fetal Movement: This is done by a trained examiner. It is easily elicited after 24 weeks of pregnancy.
- X-ray: An x-ray will identify the entire fetal skeleton by the 12th week. In utero, the fetus receives total body radiation that may lead to genetic or gonadal alterations. An x-ray is however not a recommended test for identifying pregnancy.
- Actual Delivery of an Infant: This point is Self-explanatory.
TESTS UTILIZED TO DETERMINE PREGNANCY
- Tests are based on the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) in the urine or blood.
- Urine; This test can be performed accurately 42 days after the last menstrual period or 2 weeks after the first missed period. The first urine specimen of the morning is the best one to use.
- Blood; Radioimmunoassays (RIA) can detect HCG in the blood 2 days after implantation or 5 days before the first menstrual period is missed.







0 Comments