Introduction
It is a sexually transmitted, as well as blood-borne disease caused by a DNA virus. The virus is known as hepadnavirus and can cause both acute and chronic forms of hepatitis.
Causative organism: Hepatitis B virus.
Incubation period: between 45 and 180 days.
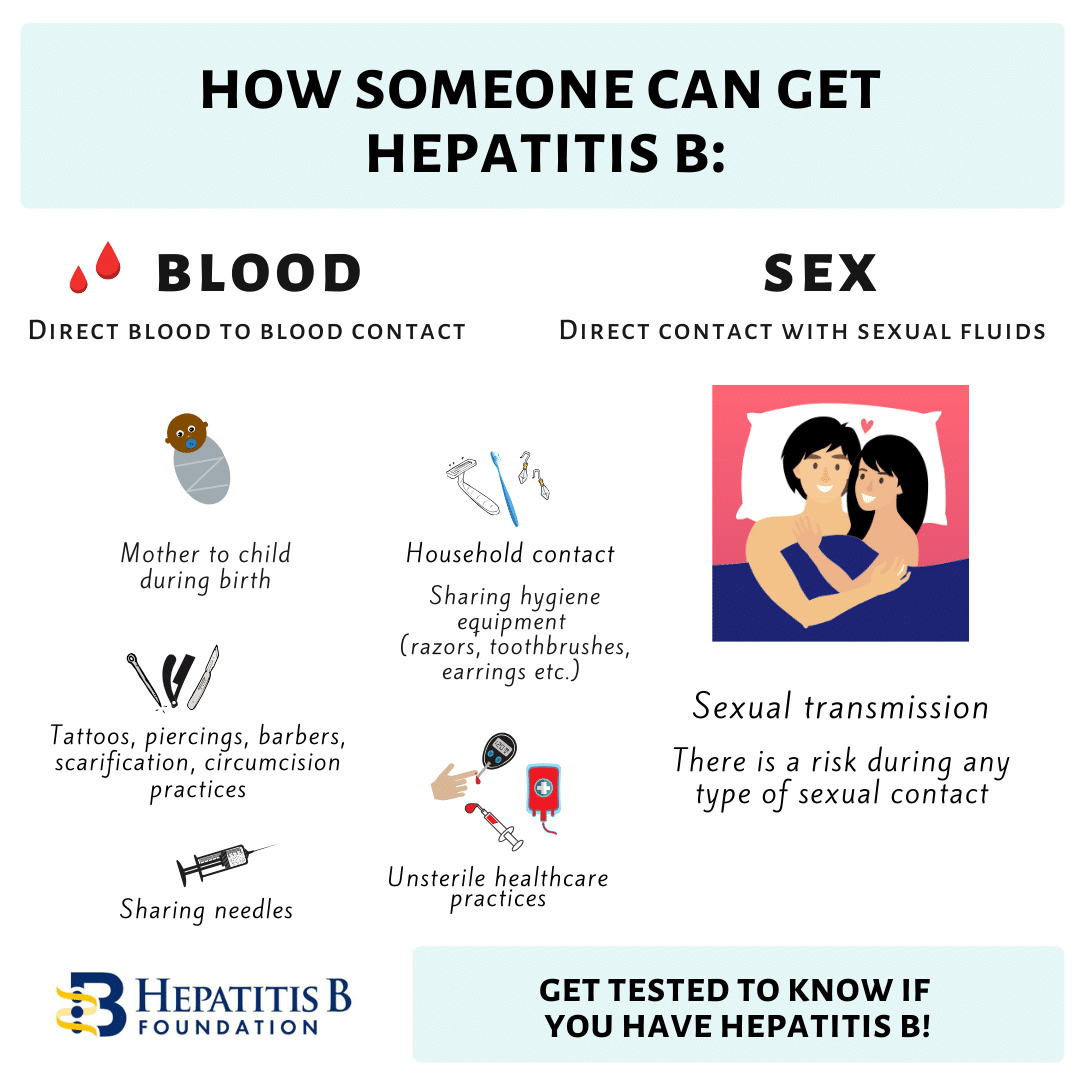
Mode of transmission
- Injection given with needles contaminated by body fluids of infected persons or carriers.
- Sexual intercourse with infected person.
- Kissing with infected persons may spread it since the virus is present in saliva.
- Transfusion with infected blood.
- Carrier mothers can transmit to their new born during the birth process.
- Indirectly from exudates from the skin ulcers of infected persons.
- Sweat and tears of infected persons have also been found to contain the virus.
Signs and Symptoms
- Prodromal period of headache, malaise, nausea, anorexia and fever for 2-14 days.
- Followed by vomiting and pain in the right hypochondria.
- Jaundice appears with variable severity after prodromal symptoms subside.
- Dark urine and pale stools.
- In most cases patient may recover completely, but there may be relapse.
- Clinically it may be difficult to distinguish between the signs and symptoms of hepatitis A and B.
Management
- There is no known treatment. Treatment is symptomatic since it is caused by a virus.
- Care providers should understand the clients, avoid being judgmental (most people attribute it to promiscuity) and give assurance of good care to them.
- Ensure enough rest.
- Give plenty of fluid especially glucose drinks, fruit drinks, water, rice water.
- Give a lot of vitamin rich foods.
Prevention and control
- Encourage abstinence until marriage and partners should be faithfully to each other to reduce the risk of being infected.
- Avoid unnecessary' casual sex exposure.
- Use condom for casual sexual intercourse if it cannot be avoided.
- Visit qualified institutions for health care to prevent contaminated articles being used for your treatment.
- Sharp and piercing instruments should be sterilized after use.
- Blood should be well screened before transfusion.
- All children should be given active immunization against the disease with DPT/HibHepB vaccine.
- Care providers and health care workers at risk should be give Hepatitis B vaccine.
- People who get exposed to the virus should be given passive immunity with hepatitis B immune vaccine.
- Some persons become life-long carriers and so must be educated to prevent infecting others.
Read Also








1 Comments
I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of the
ReplyDeleteliver already present. I started on antiviral medications which
reduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virus
became resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment from
ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC (www.ultimatelifeclinic.com) in March, 2020. Their
treatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test after
the 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazing
treatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.