201. The physician has ordered Zyvox (linezolid) for a patient
diagnosed with vancomycin resistant enterococcus. Which food should be
avoided?
A. Wheat bread
B. Honey
C. Oranges
D. Aged cheese
A. Wheat bread
B. Honey
C. Oranges
D. Aged cheese
202.
The nurse is preparing to administer a Meruvax II (rubella) vaccine to
an adult client. Which one of the following allergies contraindicates
the use of the vaccine?
A. Penicillin
B. Neomycin
C. Acyclovir
D. Tetracycline
A. Penicillin
B. Neomycin
C. Acyclovir
D. Tetracycline
203. The physician has ordered Zantac (ranitidine) for a client with reflux. The nurse should administer the medication:
A. Mid afternoon
B. Thirty minutes before eating
C. In a single dose at bedtime
D. Mid-morning
A. Mid afternoon
B. Thirty minutes before eating
C. In a single dose at bedtime
D. Mid-morning
204.
A temporary colostomy is performed on the client with colon cancer. The
nurse is aware that the proximal end of a double barrel colostomy:
A. Opens on the left side of the abdomen
B. Will produce only mucus
C. Opens on the right side of the abdomen
D. Will be bluish colored in appearance
A. Opens on the left side of the abdomen
B. Will produce only mucus
C. Opens on the right side of the abdomen
D. Will be bluish colored in appearance
205.
While assessing the postpartal client, the nurse notes that the fundus
is displaced to the right. Based on this finding, the nurse should:
A. Ask the client to void
B. Assess the blood pressure for hypotension
C. Administer oxytocin
D. Check for vaginal bleeding
A. Ask the client to void
B. Assess the blood pressure for hypotension
C. Administer oxytocin
D. Check for vaginal bleeding
206. The physician has ordered an MRI as a part of the client’s diagnostic work-up. An MRI should not be done if the client has:
A. The need for oxygen therapy
B. A history of claustrophobia
C. A permanent pacemaker
D. Sensory deafness
A. The need for oxygen therapy
B. A history of claustrophobia
C. A permanent pacemaker
D. Sensory deafness
207. Which toy is best suited to the developmental skills of a one-year-old?
A. Pounding board
B. Pull toy
C. Soft books
D. Puzzle with large pieces
A. Pounding board
B. Pull toy
C. Soft books
D. Puzzle with large pieces
208. Which of the following statements is true regarding management of the client with multiple sclerosis?
A. Taking a hot bath will decrease stiffness and spasticity.
B. A schedule of strenuous exercise will improve muscle strength.
C. Rest periods should be scheduled throughout the day.
D. Visual disturbances can be corrected with prescription glasses.
A. Taking a hot bath will decrease stiffness and spasticity.
B. A schedule of strenuous exercise will improve muscle strength.
C. Rest periods should be scheduled throughout the day.
D. Visual disturbances can be corrected with prescription glasses.
209. A client on the postpartum unit has a proctoepisiotomy. The nurse should anticipate administering which medication?
A. Dulcolax suppository
B. Docusate sodium (Colace)
C. Methylergonovine maleate (Methergine)
D. Bromocriptine sulfate (Parlodel)
A. Dulcolax suppository
B. Docusate sodium (Colace)
C. Methylergonovine maleate (Methergine)
D. Bromocriptine sulfate (Parlodel)
210.
A client with pancreatic cancer who is receiving TPN has an order for
sliding-scale insulin. The reason for the ordered insulin is:
A. TPN leads to negative nitrogen balance and elevated glucose levels.
B. TPN cannot be managed with oral hypoglycemics.
C. TPN is a high-glucose solution that can elevate the blood glucose levels.
D. TPN use can depress the activity of the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
A. TPN leads to negative nitrogen balance and elevated glucose levels.
B. TPN cannot be managed with oral hypoglycemics.
C. TPN is a high-glucose solution that can elevate the blood glucose levels.
D. TPN use can depress the activity of the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
211.
An adolescent primigravida who is 10 weeks pregnant attends the
antepartal clinic for a first check-up. To develop a teaching plan, the
nurse should initially assess:
A. The client’s knowledge of the signs of preterm labor
B. The client’s feelings about the pregnancy
C. The client’s method of birth control
D. The client’s plans for continuing school
A. The client’s knowledge of the signs of preterm labor
B. The client’s feelings about the pregnancy
C. The client’s method of birth control
D. The client’s plans for continuing school
212.
A client is admitted with a two-day history of nausea and vomiting.
Which IV fluid is appropriate for the client with moderate dehydration?
A. Lactated Ringer's
B. Dextrose 1% in water
C. Three percent normal saline
D. Dextrose 5% /.45% normal saline
A. Lactated Ringer's
B. Dextrose 1% in water
C. Three percent normal saline
D. Dextrose 5% /.45% normal saline
213. The physician has ordered a thyroid scan to confirm the diagnosis of a goiter. Before the procedure, the nurse should:
A. Assess the client for allergies to iodine
B. Bolus the client with IV fluid
C. Administer an anxiolytic
D. Insert a urinary catheter
A. Assess the client for allergies to iodine
B. Bolus the client with IV fluid
C. Administer an anxiolytic
D. Insert a urinary catheter
214.
The physician has ordered an injection of RhoGAM for a client with
blood type A negative. The nurse understands that RhoGAM is given to:
A. Provide immunity against Rh isoenzymes
B. Prevent the formation of Rh antibodies
C. Eliminate circulating Rh antibodies
D. Convert the Rh factor from negative to positive
A. Provide immunity against Rh isoenzymes
B. Prevent the formation of Rh antibodies
C. Eliminate circulating Rh antibodies
D. Convert the Rh factor from negative to positive
215.
The nurse is caring for a client admitted to the emergency room after a
fall. X-rays reveal that the client has several fractured bones in the
foot. Which treatment should the nurse anticipate for the fractured
foot?
A. Application of a walking boot
B. Stabilization with a cast
C. Surgery with Kirschner wire implantation
D. Application of spica cast
A. Application of a walking boot
B. Stabilization with a cast
C. Surgery with Kirschner wire implantation
D. Application of spica cast
216.
A client with prostate cancer is being treated with iridium seed
implants. The nurse’s discharge teaching should include telling the
client to:
A. Strain his urine
B. Increase his fluid intake
C. Report urinary frequency
D. Avoid prolonged sitting
A. Strain his urine
B. Increase his fluid intake
C. Report urinary frequency
D. Avoid prolonged sitting
217.
A patient with pulmonary tuberculosis is receiving combination therapy.
To increase the effects of the medication, the patient may be given:
A. Inderal (propranolol)
B. Dilantin (phenytoin)
C. Benemid (probenecid)
D. Neoral (cyclosporine)
A. Inderal (propranolol)
B. Dilantin (phenytoin)
C. Benemid (probenecid)
D. Neoral (cyclosporine)
218. The nurse is preparing a client for cataract surgery. The nurse is aware that:
A. Mydriatics will be used to dilate the pupil.
B. Miotics will be used to constrict the pupil.
C. A laser will be used to smooth and reshape the lens.
D. Silicone oil injections will be used to hold the retina in place.
A. Mydriatics will be used to dilate the pupil.
B. Miotics will be used to constrict the pupil.
C. A laser will be used to smooth and reshape the lens.
D. Silicone oil injections will be used to hold the retina in place.
219. A client with Alzheimer’s disease is in a skilled nursing facility. Which intervention is therapeutic for the client?
A. Placing mirrors in several locations in the facility
B. Placing a picture of the client in her room
C. Placing simple signs to indicate the location of her room, the bathroom, and dining room
D. Alternating healthcare workers to prevent boredom
A. Placing mirrors in several locations in the facility
B. Placing a picture of the client in her room
C. Placing simple signs to indicate the location of her room, the bathroom, and dining room
D. Alternating healthcare workers to prevent boredom
220.
A client with an abdominal cholecystectomy returns from surgery with a
Jackson-Pratt drain. The chief purpose of the Jackson-Pratt drain is:
A. Prevent the need for dressing changes
B. Reduce edema at the incision
C. Provide for wound drainage
D. Keep the common bile duct open
A. Prevent the need for dressing changes
B. Reduce edema at the incision
C. Provide for wound drainage
D. Keep the common bile duct open
221.
The nurse is performing an initial assessment of a newborn delivered at
32 weeks gestation. The nurse can expect to find the presence of:
A. Vernix caseosa
B. Sucking pads
C. Head lag
D. Absence of scarf sign
A. Vernix caseosa
B. Sucking pads
C. Head lag
D. Absence of scarf sign
222.
The nurse is caring for a client admitted with multiple trauma.
Fractures include the pelvis, femur, and ulna. Which finding should be
reported to the physician immediately?
A. Hematuria
B. Muscle spasms
C. Dizziness
D. Nausea
A. Hematuria
B. Muscle spasms
C. Dizziness
D. Nausea
223. A client with a history of cocaine abuse is experiencing tactile hallucinations. This symptom is known as:
A. Dyskinesia
B. Confabulation
C. Formication
D. Dystonia
A. Dyskinesia
B. Confabulation
C. Formication
D. Dystonia
224.
The nurse is preparing to suction the client with a tracheotomy. The
nurse notes a previously used bottle of normal saline on the client’s
bedside table. There is no label to indicate the date or time of initial
use. The nurse should:
A. Lip the bottle and use a pack of sterile 4×4 for the dressing
B. Obtain a new bottle and label it with the date and time of first use
C. Ask the ward secretary when the solution was requested
D. Label the existing bottle with the current date and time
A. Lip the bottle and use a pack of sterile 4×4 for the dressing
B. Obtain a new bottle and label it with the date and time of first use
C. Ask the ward secretary when the solution was requested
D. Label the existing bottle with the current date and time
225.
An infant’s Apgar score is 9 at five minutes. The nurse is aware that
the most likely cause for the deduction of one point is:
A. The newborn is hypothermic.
B. The newborn is experiencing bradycardia.
C. The newborn has acrocyanosis.
D. The newborn is lethargic.
A. The newborn is hypothermic.
B. The newborn is experiencing bradycardia.
C. The newborn has acrocyanosis.
D. The newborn is lethargic.
226. The primary reason for rapid continuous rewarming of the area affected by frostbite is to:
A. Lessen the amount of cellular damage
B. Prevent the formation of blisters
C. Promote movement
D. Prevent pain and discomfort
A. Lessen the amount of cellular damage
B. Prevent the formation of blisters
C. Promote movement
D. Prevent pain and discomfort
227.
A client recently started on hemodialysis wants to know how the
dialysis will take the place of his kidneys. The nurse’s response is
based on the knowledge that hemodialysis works by:
A. Passing water through a dialyzing membrane
B. Eliminating plasma proteins from the blood
C. Lowering the pH by removing nonvolatile acids
D. Filtering waste through a dialyzing membrane
A. Passing water through a dialyzing membrane
B. Eliminating plasma proteins from the blood
C. Lowering the pH by removing nonvolatile acids
D. Filtering waste through a dialyzing membrane
228.
A client hospitalized with AIDS tells the nurse that he has been
exposed to measles. The nurse should contact the physician regarding an
order for:
A. An antibiotic
B. Immune globulin
C. An antiviral
D. Airborne isolation
A. An antibiotic
B. Immune globulin
C. An antiviral
D. Airborne isolation
229.
A client hospitalized with MRSA is placed on contact precautions. Which
statement is true regarding precautions for infections spread by
contact?
A. The client should be placed in a room with negative pressure.
B. Infection requires close contact; therefore, the door may remain open.
C. Transmission is highly likely, so the client should wear a mask at all times.
D. Infection requires skin-to-skin contact and is prevented by hand washing, gloves, and a gown.
A. The client should be placed in a room with negative pressure.
B. Infection requires close contact; therefore, the door may remain open.
C. Transmission is highly likely, so the client should wear a mask at all times.
D. Infection requires skin-to-skin contact and is prevented by hand washing, gloves, and a gown.
230.
A client who is admitted with an above-the-knee amputation tells the
nurse that his foot hurts and itches. Which response by the nurse
indicates understanding of phantom limb pain?
A. The pain will go away in a few days.
B. The pain is due to peripheral nervous system interruptions. I will get you some pain medication.
C. The pain is psychological because your foot is no longer there.
D. The pain and itching are due to the infection you had before the surgery.
A. The pain will go away in a few days.
B. The pain is due to peripheral nervous system interruptions. I will get you some pain medication.
C. The pain is psychological because your foot is no longer there.
D. The pain and itching are due to the infection you had before the surgery.
231. A client with cancer of the pancreas has undergone a Whipple procedure. The Whipple procedure includes the removal of:
A. The head of the pancreas
B. The proximal third of the small intestine
C. The stomach and duodenum
D. The esophagus and jejunum
A. The head of the pancreas
B. The proximal third of the small intestine
C. The stomach and duodenum
D. The esophagus and jejunum
232.
The physician has ordered a minimal-bacteria diet for a client with
neutropenia. The client should be taught to avoid using which condiment?
A. Mustard
B. Salt
C. Pepper
D. Ketchup
A. Mustard
B. Salt
C. Pepper
D. Ketchup
233. A client is discharged home with a prescription for Coumadin (sodium warfarin). The client should be instructed to:
A. Avoid antihistamines containing diphenhydramine
B. Increase the intake of all vegetables
C. Have a PTT checked monthly
D. Have a CBC drawn every six months
A. Avoid antihistamines containing diphenhydramine
B. Increase the intake of all vegetables
C. Have a PTT checked monthly
D. Have a CBC drawn every six months
234.
The nurse is assisting the physician with removal of a central venous
catheter. To facilitate removal, the nurse should instruct the client
to:
A. Take a deep breath, hold it, and bear down as the catheter is withdrawn
B. Turn his head to the left side and hyperextend the neck
C. Take slow, deep breaths as the catheter is removed
D. Turn his head to the right while maintaining a sniffing position
A. Take a deep breath, hold it, and bear down as the catheter is withdrawn
B. Turn his head to the left side and hyperextend the neck
C. Take slow, deep breaths as the catheter is removed
D. Turn his head to the right while maintaining a sniffing position
235. A client has an order for streptokinase. Before administering the medication, the nurse should assess the client for:
A. Allergies to pineapples and bananas
B. A history of streptococcal infections
C. Prior therapy with phenytoin
D. A history of alcohol abuse
A. Allergies to pineapples and bananas
B. A history of streptococcal infections
C. Prior therapy with phenytoin
D. A history of alcohol abuse
236. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for the client with leukemia. The client should be told to avoid:
A. Using oils or cream-based soaps
B. Flossing between the teeth
C. The intake of salt
D. Using an electric razor
A. Using oils or cream-based soaps
B. Flossing between the teeth
C. The intake of salt
D. Using an electric razor
237.
The nurse is changing the ties of the client with a tracheostomy. The
safest method of changing the tracheostomy ties is to:
A. Apply the new tie before removing the old one
B. Have a helper present in case assistance is needed
C. Hold the tracheostomy tie with the nondominant hand while removing the old tie
D. Ask the client to hold the tracheostomy in place as the ties are changed
A. Apply the new tie before removing the old one
B. Have a helper present in case assistance is needed
C. Hold the tracheostomy tie with the nondominant hand while removing the old tie
D. Ask the client to hold the tracheostomy in place as the ties are changed
238.
The nurse is monitoring a client following a lung resection. The hourly
output from the mediastinal tube was 300mL. The nurse should give
priority to:
A. Turning the client to the left side
B. Milking the tube to ensure patency
C. Slowing the intravenous infusion
D. Notify the physician of the amount
A. Turning the client to the left side
B. Milking the tube to ensure patency
C. Slowing the intravenous infusion
D. Notify the physician of the amount
239.
An infant with congenital heart disease is admitted with symptoms of
congestive heart failure. Which of the following is a sign of fluid
overload in the infant?
A. Bulging fontanels
B. Bradycardia
C. Urine specific gravity of 1.015
D. Bradypnea
A. Bulging fontanels
B. Bradycardia
C. Urine specific gravity of 1.015
D. Bradypnea
240.
The nurse is educating the lady’s club in self-breast exam. The nurse
is aware that most malignant breast masses occur in the tail of Spence.
On the diagram, place an X on the tail of Spence.
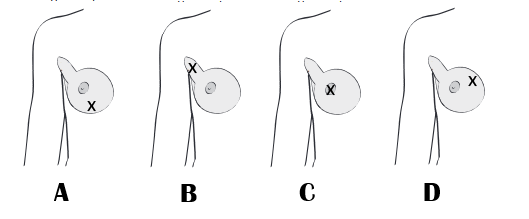
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D

A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
241. A toddler is admitted for the repair of a VSD. The nurse is aware that the child with a VSD will:
A. Tire more easily
B. Have normal patterns of growth and development
C. Require more calories
D. Need additional fluids to prevent thrombi
A. Tire more easily
B. Have normal patterns of growth and development
C. Require more calories
D. Need additional fluids to prevent thrombi
242.
An obstetrical client with a history of stillbirths has an order for a
nonstress test. The nurse is aware that a nonstress test is ordered to:
A. Determine lung maturity
B. Measure the fetal activity
C. Show the effect of contractions on fetal heart rate
D. Measure the well-being of the fetus
A. Determine lung maturity
B. Measure the fetal activity
C. Show the effect of contractions on fetal heart rate
D. Measure the well-being of the fetus
243.
The nurse is evaluating the client who was admitted eight hours ago for
induction of labor. The following graph is noted on the monitor. Which
action should be taken first by the nurse?
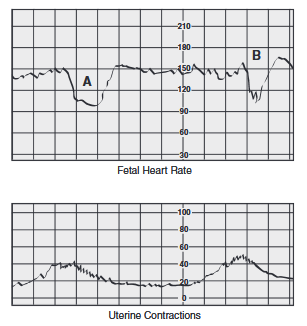
A. Instruct the client to push
B. Perform a vaginal exam
C. Stop the infusion of Pitocin (oxytocin)
D. Place the client in a semi-Fowler’s position

A. Instruct the client to push
B. Perform a vaginal exam
C. Stop the infusion of Pitocin (oxytocin)
D. Place the client in a semi-Fowler’s position
244. The nurse notes the following on the ECG monitor. The nurse would evaluate the cardiac arrhythmia as:

A. Atrial flutter
B. A sinus rhythm
C. Ventricular tachycardia
D. Atrial fibrillation

A. Atrial flutter
B. A sinus rhythm
C. Ventricular tachycardia
D. Atrial fibrillation
245. Which instruction should be given to the client who is self-administering Lovenox (enoxaparin)?
A. Inject the medication into the deltoid muscle
B. Inject the medication into the abdomen
C. Aspirate before administering the medication
D. Clear the air from the syringe before administering the medication
A. Inject the medication into the deltoid muscle
B. Inject the medication into the abdomen
C. Aspirate before administering the medication
D. Clear the air from the syringe before administering the medication
246.
The nurse has a preoperative order to administer Valium (diazepam) 10mg
and Phenergan (promethazine) 25mg. The correct method of administering
these medications is to:
A. Administer the medications together in one syringe
B. Administer the medications separately
C. Administer the Valium, wait five minutes, and then administer the Phenergan
D. Question the order because the medications should not be given to the same patient
A. Administer the medications together in one syringe
B. Administer the medications separately
C. Administer the Valium, wait five minutes, and then administer the Phenergan
D. Question the order because the medications should not be given to the same patient
247.
A female client with a history of frequent urinary tract infections
asks the nurse how she can reduce the risk of recurrence. The nurse
should tell the client to:
A. Douche after intercourse
B. Void every three hours
C. Increase her intake of foods containing vitamin C
D. Wipe from back to front after voiding
A. Douche after intercourse
B. Void every three hours
C. Increase her intake of foods containing vitamin C
D. Wipe from back to front after voiding
248. Which task is within the scope of practice of the nursing assistant?
A. Obtaining vital signs on a patient following a craniotomy
B. Obtaining hourly intake and output on a client with preeclampsia
C. Feeding the client with depression
D. Ambulating the client following a hip replacement
A. Obtaining vital signs on a patient following a craniotomy
B. Obtaining hourly intake and output on a client with preeclampsia
C. Feeding the client with depression
D. Ambulating the client following a hip replacement
249. Which finding indicates a complication following a parathyroidectomy?
A. Two-inch circle of blood behind the neck
B. Eupnea
C. Absence of carpopedal spasms
D. Negative Chvostek’s sign
A. Two-inch circle of blood behind the neck
B. Eupnea
C. Absence of carpopedal spasms
D. Negative Chvostek’s sign
250.
The physician has ordered amphotericin B for a client with
histoplasmosis. In order to reduce the risk of nephrotoxicity, the nurse
should:
A. Premedicate the patient with diphenhydramine and acetaminophen.
B. Test for hypersensitivity prior to administration.
C. Administer with heparin and hydrocortisone over four to six hours.
D. Hydrate with IV fluids before and after the drug is administered.
A. Premedicate the patient with diphenhydramine and acetaminophen.
B. Test for hypersensitivity prior to administration.
C. Administer with heparin and hydrocortisone over four to six hours.
D. Hydrate with IV fluids before and after the drug is administered.
251. A client with a renal failure is prescribed a low potassium diet. Which food choice would be best for this client?
A. 1 cup beef broth
B. 1 baked potato with the skin
C. 1/2 cup raisins
D. 1 cup rice
A. 1 cup beef broth
B. 1 baked potato with the skin
C. 1/2 cup raisins
D. 1 cup rice
252. An appropriate nursing intervention for the client with borderline personality disorder is:
A. Observing the client for signs of depression or suicidal thinking
B. Allowing the client to lead unit group sessions
C. Restricting the client’s activity to the assigned unit of care throughout hospitalization
D. Allowing the client to select a primary caregiver
A. Observing the client for signs of depression or suicidal thinking
B. Allowing the client to lead unit group sessions
C. Restricting the client’s activity to the assigned unit of care throughout hospitalization
D. Allowing the client to select a primary caregiver
253. Which of the following is an expected finding in the assessment of a client with bulimia nervosa?
A. Extreme weight loss
B. Presence of lanugo over body
C. Erosion of tooth enamel
D. Muscle wasting
A. Extreme weight loss
B. Presence of lanugo over body
C. Erosion of tooth enamel
D. Muscle wasting
254.
Assuming that all have achieved normal cognitive and emotional
development, which of the following children is at greatest risk for
accidental poisoning?
A. One-year-old
B. Four-year-old
C. Eight-year-old
D. Twelve-year-old
A. One-year-old
B. Four-year-old
C. Eight-year-old
D. Twelve-year-old
255. Which term describes the play activity of the preschool aged child?
A. Cooperative
B. Associative
C. Parallel
D. Solitary
A. Cooperative
B. Associative
C. Parallel
D. Solitary
256.
The nurse is ready to begin an exam on a nine-month-old infant who is
sitting quietly on his mother’s lap. Which should the nurse do first?
A. Check the Babinski reflex
B. Listen to the heart and lung sounds
C. Palpate the abdomen
D. Check tympanic membranes
A. Check the Babinski reflex
B. Listen to the heart and lung sounds
C. Palpate the abdomen
D. Check tympanic membranes
257. In terms of cognitive development, a three-year-old would be expected to:
A. Think abstractly
B. Use magical thinking
C. Understand conservation of matter
D. See things from the perspective of others
A. Think abstractly
B. Use magical thinking
C. Understand conservation of matter
D. See things from the perspective of others
258. Which of the following describes the language development of a two-year-old?
A. Doesn’t understand yes and no
B. Understands the meaning of all words
C. Can combine three or four words
D. Repeatedly asks “why?”
A. Doesn’t understand yes and no
B. Understands the meaning of all words
C. Can combine three or four words
D. Repeatedly asks “why?”
259.
A client who has been receiving Urokinase (uPA) for deep vein
thrombosis is noted to have dark brown urine in the urine collection
bag. Which action should the nurse take immediately?
A. Prepare an injection of vitamin K
B. Irrigate the urinary catheter with 50 mL of normal saline
C. Offer the client additional oral fluids
D. Withhold the medication and notify the physician
A. Prepare an injection of vitamin K
B. Irrigate the urinary catheter with 50 mL of normal saline
C. Offer the client additional oral fluids
D. Withhold the medication and notify the physician
260. Which of the following can occur with the frequent use of calcium-based antacids?
A. Constipation
B. Hyperperistalsis
C. Delayed gastric emptying
D. Diarrhea
A. Constipation
B. Hyperperistalsis
C. Delayed gastric emptying
D. Diarrhea
261. Which statement made by the student nurse indicates the need for further teaching regarding the administration of heparin?
A. I will administer the medication 1–2 inches away from the umbilicus.
B. I will not massage the injection site after administering the heparin.
C. I will check the PTT before administering the heparin.
D. I will need to gently aspirate when I give the heparin.
A. I will administer the medication 1–2 inches away from the umbilicus.
B. I will not massage the injection site after administering the heparin.
C. I will check the PTT before administering the heparin.
D. I will need to gently aspirate when I give the heparin.
262. To correctly assess the oxygen saturation level of an adult client, the pulse oximeter should not be placed on the:
A. Finger
B. Earlobe
C. Extremity with noninvasive BP cuff
D. Nose
A. Finger
B. Earlobe
C. Extremity with noninvasive BP cuff
D. Nose
263.
While caring for an elderly patient with hypertension, the nurse notes
the following vital signs: BP of 140/40, pulse 120, respirations 36. The
nurse’s initial action should be to:
A. Report the findings to the physician
B. Recheck the vital signs in one hour
C. Ask the patient if he is in pain
D. Compare the current vital signs with those on admission
A. Report the findings to the physician
B. Recheck the vital signs in one hour
C. Ask the patient if he is in pain
D. Compare the current vital signs with those on admission
264. The nurse is preparing a client with an axillopopliteal bypass graft for discharge. The client should be taught to avoid:
A. Using a recliner to rest
B. Resting in supine position
C. Sitting in a straight chair
D. Sleeping in right Sim’s position
A. Using a recliner to rest
B. Resting in supine position
C. Sitting in a straight chair
D. Sleeping in right Sim’s position
265.
The doctor has ordered antithrombotic stockings to be applied to the
legs of a client with peripheral vascular disease. The nurse knows
antithrombotic stockings should be applied:
A. Before the client arises in the morning
B. With the client in a standing position
C. After the client has bathed and applied lotion to the legs
D. Before the client retires in the evening
A. Before the client arises in the morning
B. With the client in a standing position
C. After the client has bathed and applied lotion to the legs
D. Before the client retires in the evening
266.
The nurse has just received the change of shift report and is preparing
to make rounds. Which client should the nurse assess first?
A. A client recovering from a stroke with an oxygen saturation rate of 99%
B. A client three days post-coronary artery bypass graft with an oral temperature of 100.2ºF
C. A client admitted one hour ago with rales and shortness of breath
D. A client being prepared for discharge following a right colectomy
A. A client recovering from a stroke with an oxygen saturation rate of 99%
B. A client three days post-coronary artery bypass graft with an oral temperature of 100.2ºF
C. A client admitted one hour ago with rales and shortness of breath
D. A client being prepared for discharge following a right colectomy
267.
A client with a femoral popliteal bypass graft is assigned to a
semiprivate room. The most suitable roommate for this client is the
client with:
A. Hypothyroidism
B. Diabetic ulcers
C. Gastroenteritis
D. Bacterial pneumonia
A. Hypothyroidism
B. Diabetic ulcers
C. Gastroenteritis
D. Bacterial pneumonia
268.
The nurse is teaching the client regarding use of sodium warfarin.
Which statement made by the client would require further teaching?
A. I will have blood drawn every month.
B. I will assess my skin for a rash.
C. I take aspirin for a headache.
D. I will use an electric razor to shave.
A. I will have blood drawn every month.
B. I will assess my skin for a rash.
C. I take aspirin for a headache.
D. I will use an electric razor to shave.
269.
The client returns to the recovery room following repair of an
abdominal aneurysm. Which finding would require further investigation?
A. Pedal pulses regular
B. Urinary output 20mL in the past hour
C. Blood pressure 108/50
D. Oxygen saturation 97%
A. Pedal pulses regular
B. Urinary output 20mL in the past hour
C. Blood pressure 108/50
D. Oxygen saturation 97%
270.
The nurse is doing bowel and bladder retraining for the client with
paraplegia. Which of the following is not a factor for the nurse to
consider?
A. Diet pattern
B. Mobility
C. Fluid intake
D. Sexual function
A. Diet pattern
B. Mobility
C. Fluid intake
D. Sexual function
271. Which one of the following statements is correct when measuring the client for crutches?
A. A distance of five fingerbreadths should exist between the top of the crutch and the axilla.
B. The nurse should measure three inches between the top of the crutch and the axilla.
C. The client’s elbows should be flexed at a 10º angle.
D. The crutches should be extended 8 to 10 inches from the side of the foot.
A. A distance of five fingerbreadths should exist between the top of the crutch and the axilla.
B. The nurse should measure three inches between the top of the crutch and the axilla.
C. The client’s elbows should be flexed at a 10º angle.
D. The crutches should be extended 8 to 10 inches from the side of the foot.
272.
The nurse is caring for a client following a cerebral vascular
accident. Which portion of the brain is responsible for changes in the
client’s vision?
A. Temporal lobe
B. Frontal lobe
C. Occipital lobe
D. Parietal lobe
A. Temporal lobe
B. Frontal lobe
C. Occipital lobe
D. Parietal lobe
273.
A client with a hemorrhagic stroke has a temperature of 103ºF. Efforts
to reduce the temperature have not been effective. The most likely
explanation for the elevated temperature is that damage has occurred to
the:
A. Hypothalamus
B. Pituitary
C. Carotid baroreceptors
D. Frontal lobe
A. Hypothalamus
B. Pituitary
C. Carotid baroreceptors
D. Frontal lobe
274.
A client is admitted to the hospital in chronic renal failure. A low
protein diet is ordered. The rationale for a low protein diet is that:
A. A low protein diet helps reduce blood urea nitrogen and other wastes excreted by the kidneys.
B. A low protein diet increases the sodium and potassium levels.
C. A low protein diet increases albumin production.
D. A low protein diet increases the calcium and phosphorous levels.
A. A low protein diet helps reduce blood urea nitrogen and other wastes excreted by the kidneys.
B. A low protein diet increases the sodium and potassium levels.
C. A low protein diet increases albumin production.
D. A low protein diet increases the calcium and phosphorous levels.
275. The nurse has an order for the administration of intravenous heparin. The medication should be administered using a/an:
A. Metered chamber
B. Infusion controller
C. Intravenous filter
D. Three-way stopcock
A. Metered chamber
B. Infusion controller
C. Intravenous filter
D. Three-way stopcock
276.
When assessing the client’s blood pressure, the nurse should use a cuff
with a width that is ____% of the circumference of the extremity. (Fill
in the blank.)
A. 40
B. 30
C. 20
D. 10
A. 40
B. 30
C. 20
D. 10
277. Which diet would the nurse expect to see ordered for a patient with nephrotic syndrome?
A. Low carbohydrate potassium
B. Moderate protein
C. Low calcium
D. Increased potassium
A. Low carbohydrate potassium
B. Moderate protein
C. Low calcium
D. Increased potassium
278.
A client with an abdominal aortic aneurysm is admitted in preparation
for surgery. Which finding should be reported to the doctor?
A. A WBC of 14,000 cu.mm
B. Auscultation of abdominal bruit
C. Complaints of lower back pain
D. A platelet count of 175,000 cu.mm
A. A WBC of 14,000 cu.mm
B. Auscultation of abdominal bruit
C. Complaints of lower back pain
D. A platelet count of 175,000 cu.mm
279.
When assessing deep tendon reflexes, the nurse grades the client’s
patellar reflex as a 3+. This reading indicates that the assessed reflex
is:
A. Stronger than normal
B. Hypoactive
C. Normal
D. Hyperactive
A. Stronger than normal
B. Hypoactive
C. Normal
D. Hyperactive
280.
The physician has ordered atropine sulfate 0.4milligrams IM before
surgery. The medication is supplied in 0.8 milligrams per milliliter.
How much medication should the nurse prepare to administer?
A. 0.25mL
B. 0.5mL
C. 1.0mL
D. 1.25mL
A. 0.25mL
B. 0.5mL
C. 1.0mL
D. 1.25mL
281. The nurse is evaluating the client’s pulmonary artery pressure (PAP). The nurse is aware that PAP evaluates:
A. Pressure in the left ventricle
B. Systolic, diastolic, and mean pressure in the pulmonary artery
C. Pressure in the pulmonary veins
D. Pressure in the right ventricle
A. Pressure in the left ventricle
B. Systolic, diastolic, and mean pressure in the pulmonary artery
C. Pressure in the pulmonary veins
D. Pressure in the right ventricle
282. A client is being monitored using a central venous pressure monitor. If the CVP is 1 cm of water, the nurse should:
A. Notify the physician immediately
B. Slow the intravenous infusion
C. Auscultate the lungs for rales
D. Administer a diuretic
A. Notify the physician immediately
B. Slow the intravenous infusion
C. Auscultate the lungs for rales
D. Administer a diuretic
283.
The nurse identifies ventricular tachycardia on the cardiac monitor.
The patient has a pulse rate of 160 with a regular rhythm. The nurse
should give priority to:
A. Administering atropine sulfate
B. Requesting a stat potassium level
C. Administering amiodarone
D. Defibrillating at 360 joules
A. Administering atropine sulfate
B. Requesting a stat potassium level
C. Administering amiodarone
D. Defibrillating at 360 joules
284. In preparation for the removal of the client’s chest tubes, the nurse should instruct the client to:
A. Breathe normally
B. Hold his breath and bear down
C. Take deep breaths
D. Take shallow breaths
A. Breathe normally
B. Hold his breath and bear down
C. Take deep breaths
D. Take shallow breaths
285.
An elderly patient has been taking 80mg of furosemide (Lasix) bid. The
nurse notes that the patient’s most recent potassium level is 2.5mEq/L.
The nurse should:
A. Continue the medication as ordered
B. Administer the morning dose only
C. Give the medication with orange juice
D. Withhold the medication and notify the physician
A. Continue the medication as ordered
B. Administer the morning dose only
C. Give the medication with orange juice
D. Withhold the medication and notify the physician
286.
Which one of the following lab tests should be done periodically if the
client is being maintained on warfarin sodium (Coumadin)?
A. Platelet count
B. White blood cell count
C. Neutrophil count
D. Basophil count
A. Platelet count
B. White blood cell count
C. Neutrophil count
D. Basophil count
287. Which statement is true regarding therapy with Levemir (insulin detemir)?
A. The onset is 1–2 hours.
B. It may be mixed with regular insulin.
C. It peaks in 2–3 hours.
D. The duration is 24 hours.
A. The onset is 1–2 hours.
B. It may be mixed with regular insulin.
C. It peaks in 2–3 hours.
D. The duration is 24 hours.
288.
A client with AIDS tells the nurse that he has been using herbal
supplements in addition to the regimen of drugs prescribed by the
physician. The nurse should tell the client that:
A. Most herbals are well suited to use with prescription medications.
B. He should buy only FDA-approved herbal supplements for use.
C. The use of herbals may alter the effect of the medication he is taking.
D. The herbal supplements should be taken at the same time as his medication.
A. Most herbals are well suited to use with prescription medications.
B. He should buy only FDA-approved herbal supplements for use.
C. The use of herbals may alter the effect of the medication he is taking.
D. The herbal supplements should be taken at the same time as his medication.
289.
The nurse is assessing the vital signs of a client with pancreatic
cancer. In addition to routine vital signs, the nurse assesses the fifth
vital sign of:
A. Anorexia
B. Pain
C. Insomnia
D. Fatigue
A. Anorexia
B. Pain
C. Insomnia
D. Fatigue
290.
The physician has prescribed Oxycontin (oxycodone) for a client
following an exploratory laparotomy. Which of the following is an
adverse effect associated with the medication?
A. Pulmonary edema
B. Increased blood pressure
C. Nervousness
D. Rapid pulse
A. Pulmonary edema
B. Increased blood pressure
C. Nervousness
D. Rapid pulse
291.
A patient with a PCA pump (patient controlled analgesia) asks the nurse
if he can become overdosed with pain medication using this machine.
Which statement made by the nurse is correct?
A. The machine will administer only the amount of medication needed to control pain without any action from you.
B. The machine has a locking device that prevents overdosing.
C. The machine will administer one large dose every four hours to relieve your pain.
D. The machine is set to deliver medication only if you need it.
A. The machine will administer only the amount of medication needed to control pain without any action from you.
B. The machine has a locking device that prevents overdosing.
C. The machine will administer one large dose every four hours to relieve your pain.
D. The machine is set to deliver medication only if you need it.
292. Which information should be given to the client using a TENS unit?
A. Electrocution may occur if you use water with this unit.
B. Skin irritation may occur with prolonged use of the unit.
C. The unit can be placed anywhere on the body without fear of adverse reactions.
D. A cream or lotion should be applied to the skin before applying the unit.
A. Electrocution may occur if you use water with this unit.
B. Skin irritation may occur with prolonged use of the unit.
C. The unit can be placed anywhere on the body without fear of adverse reactions.
D. A cream or lotion should be applied to the skin before applying the unit.
293.
During an intake assessment, the nurse asks the client if he has an
advanced directive. The reason for asking the client this question is:
A. The nursing staff needs to know about funeral arrangements.
B. Much confusion regarding care can occur with the client’s family if there is no advanced directive.
C. An advanced directive allows the medical personnel to make decisions for the client.
D. An advanced directive allows active euthanasia to be carried out.
A. The nursing staff needs to know about funeral arrangements.
B. Much confusion regarding care can occur with the client’s family if there is no advanced directive.
C. An advanced directive allows the medical personnel to make decisions for the client.
D. An advanced directive allows active euthanasia to be carried out.
294. Which measure helps reduce nipple soreness associated with breastfeeding?
A. Feeding the baby during the first 48 hours after delivery
B. Placing a finger between the baby’s mouth and the breast to break suction after feeding
C. Applying warm, moist soaks to the breast several times per day
D. Wearing a support bra during the day
A. Feeding the baby during the first 48 hours after delivery
B. Placing a finger between the baby’s mouth and the breast to break suction after feeding
C. Applying warm, moist soaks to the breast several times per day
D. Wearing a support bra during the day
295.
The nurse is performing an assessment on an elderly client who had a
total hip repair this morning. Which assessment finding indicates that
the patient is in pain?
A. The client’s blood pressure is 130/86.
B. The client is unable to concentrate.
C. The client’s pupils are dilated.
D. The client grimaces during care.
A. The client’s blood pressure is 130/86.
B. The client is unable to concentrate.
C. The client’s pupils are dilated.
D. The client grimaces during care.
296.
An obstetrical client decides to have epidural anesthesia to relieve
pain during labor and delivery. Following administration of the epidural
anesthesia, the nurse should monitor the client for:
A. Seizures
B. Postural hypertension
C. Respiratory depression
D. Hematuria
A. Seizures
B. Postural hypertension
C. Respiratory depression
D. Hematuria
297. Which of the following is a late sign associated with oral cancer?
A. Warmth
B. Odor
C. Pain
D. Ulcer with flat edges
A. Warmth
B. Odor
C. Pain
D. Ulcer with flat edges
298. Which complaint is frequently expressed by a client with macular degeneration?
A. Problems with activities requiring focused vision such as sewing
B. Severe eye and face pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting
C. Seeing halos around lights
D. Veil-like loss of vision
A. Problems with activities requiring focused vision such as sewing
B. Severe eye and face pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting
C. Seeing halos around lights
D. Veil-like loss of vision
299.
Continuous bladder irrigations are ordered for a patient following a
TURP. The purpose of continuous bladder irrigations is to:
A. Prevent formation of blood clots
B. Administer intravesical medication
C. Prevent postoperative pain
D. Maintain bladder tone
A. Prevent formation of blood clots
B. Administer intravesical medication
C. Prevent postoperative pain
D. Maintain bladder tone
300. The nurse is caring for a patient following a thyroidectomy. Which of the following is an early symptom of hypocalcemia?
A. Positive Chvostek’s sign
B. 3+ deep tendon reflexes
C. Numbness or tingling of the toes and extremities
D. Prolonged ST and QT intervals
A. Positive Chvostek’s sign
B. 3+ deep tendon reflexes
C. Numbness or tingling of the toes and extremities
D. Prolonged ST and QT intervals






0 Comments