Introduction
It is a highly contagious viral infection producing various symptoms and characteristic rash.
Causative organism: Morbilli virus (measles virus).
Incubation period: 7-14days
Mode of transmission
Directly by droplets spread through coughing, taking, spiting from infected persons Indirect: through freshly soiled articles from throat and nose secretion from infected individuals.
Signs and symptoms
Prodromal symptoms include;
- Fever
- Headache
- Malaise
- Convulsions
Skin: rashes begins on the face or below or in front of the ears. The rash spread within 1-2 days to the trunk, arms, and legs.
Gastrointestinal
Tract:
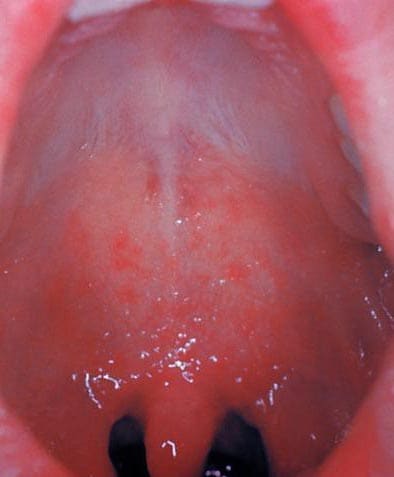 |
| Photo by CDC |
- Koplik’s spot (tiny white spots in the month)
- Loss of appetite
- Redness and soreness
- Diarrhea
Eyes: conjunctivitis and redness of the eyes.
| Photo by USC Roski Eye Institute - Keck Medicine of USC |
Management
- Isolate the patient
- Give Symptomatic treatment
- Antibiotics for secondary bacterial infection
- Tepid sponge the patient
- Apply gentian violet solution (because of sores)
- Bath child and apply soothing pomade.
- Provide Nourishing diet.
Prevention and Control
- Isolate infected individuals.
- All contacts should be isolated and observed for signs
- Concurrent disinfection of articles of infected persons
- Measles immunization at 9months. During outbreaks, it should be given at 6months and repeated at 1 year
Read Also








0 Comments